 |
|
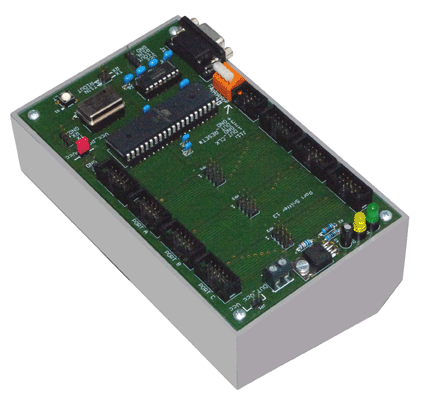
Projects: The Port Sniffer
|
|
|
|
The port sniffer is a microcontroller module to be inserted in the connections between a microcontroller (or an FPGA, for example) and the attached peripherals. Its main purpose is logging and visualization. In other words, it is (connected to a personal computer) a very basic logic analyzer. It is some kind of a probe pod. The microcontroller can observe the signal lines. It can also inject signals, or it can be programmed as a substitute, emulating the peripheral devices attached to the target system. One module can inspect up to 24 I/O signals. If more signals are to be observed, some modules can be connected to a multiprocessor hub (active or passive).
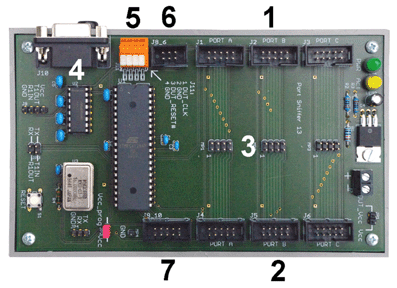
1 – inbound port signals; 2 – outbound port signals; 3 – test points; 4 – RS-232 interface; 5 – reset and clock signals for single-stepping the target system; 6 – header for multiprocessor connection (downstream / slave); 7 – header for SPI programming. The SPI port can be used alternatively to attach peripheral controllers (e.g., Ethernet) or serial memory.
|
|
|
|
September 26, 2014 The web page has been set up. |